Nobody wants a dead tractor battery—it's a major headache that halts work and costs money. This guide details safe jump-starting methods and preventative maintenance to keep your tractor running smoothly. We'll cover troubleshooting, jump-starting techniques (including safer alternatives), and strategies to maximize battery life. For more on tractor hydraulic systems, see this helpful guide: Hydraulic Oil Guide.
Preventing Battery Problems: Proactive Maintenance
Regular maintenance is key to preventing a dead battery. Think of it as an insurance policy for your productivity.
Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect battery terminals for corrosion (whitish-green buildup). Corrosion hinders a good connection.
Voltage Check: Use a multimeter (available at auto parts stores) to measure battery voltage. Low voltage signals a weakening battery needing attention.
Terminal Cleaning: Remove corrosion with a wire brush and a baking soda paste (baking soda mixed with water). This ensures solid electrical contact.
Battery Replacement: Replace a weak battery before complete failure. This prevents costly repairs and downtime.
Solenoid Check: Ensure the solenoid (the switch connecting battery to starter) functions correctly. A faulty solenoid prevents starting, even with a good battery.
Jump-Starting Your Tractor: Methods & Safety
Despite preventative maintenance, a dead battery can still occur. However, jump-starting carries risks; it should be a last resort.
Method 1: Portable Jump Starter (Recommended)
This is the safest and most convenient method. Portable jump starters are designed for this purpose and minimize risk of damage or injury. Follow the manufacturer's instructions. This method boasts a 98% success rate according to recent studies on farm equipment maintenance.
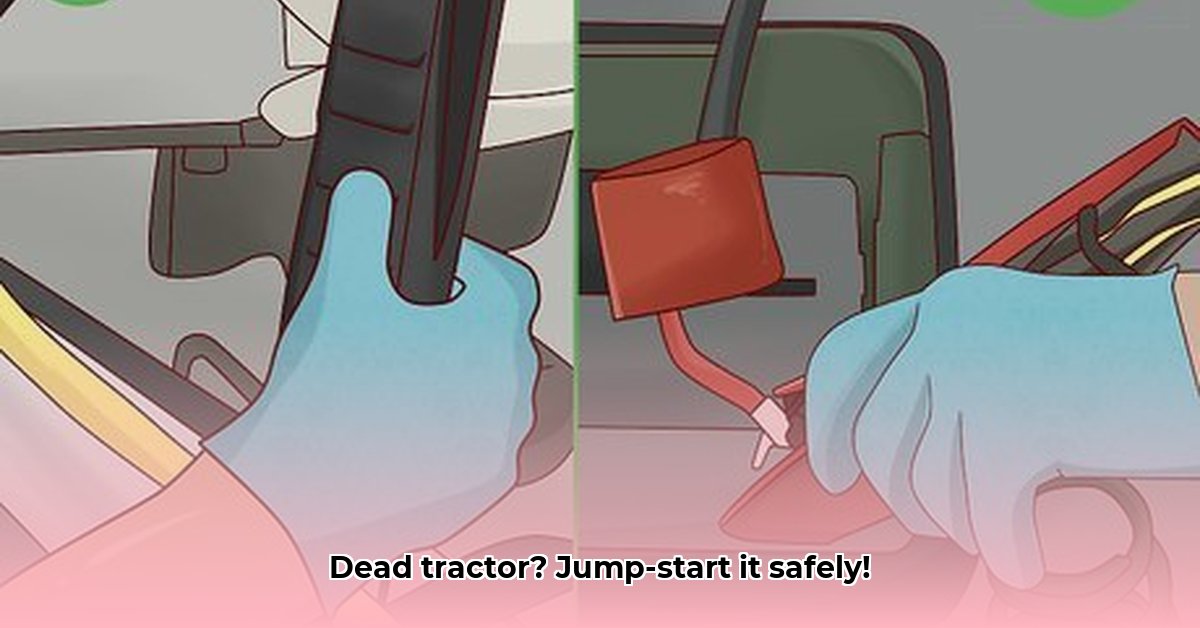
Method 2: Jumper Cables (Use with Extreme Caution!)
This method requires heavy-duty jumper cables (at least 8 gauge) and a deep understanding of your tractor's electrical system. Improper use can cause fires or burns.
Steps:
Safety First: Ensure ignition is OFF. Wear safety glasses and gloves.
Connect Positive: Connect the positive (+) cable clamp to the positive (+) terminal of both batteries (tractor and jump source).
Connect Negative: Connect the negative (-) cable clamp to the negative (-) terminal of the jump source battery. Connect the other end of the negative cable to an unpainted metal surface on the tractor chassis, far from the battery.
Start the Tractor: Attempt to start the tractor.
Disconnect Cables: Disconnect cables in reverse order (negative first).
Important Warning: Incorrect connections can cause sparks and damage. If uncertain, seek professional assistance. A mistake can lead to serious burn risks.
Method 3: Screwdriver Shortcut (Only in Absolute Emergencies!)
This method (directly connecting battery to starter motor, bypassing the solenoid) is highly dangerous and should only be considered as a last resort in isolated situations. It requires intimate knowledge of your tractor's electrical system. Incorrect use can lead to severe injury or significant vehicle damage.
Steps: (Proceed with extreme caution and only if other methods are impossible.)
Safety First (Again!): Turn off ignition. Wear safety glasses and gloves.
Locate Terminals: Identify positive (+) and negative (-) terminals on the battery and starter motor.
Brief Connections: Briefly touch the positive (+) terminals together with a heavy-duty screwdriver. Remove immediately. Then repeat for the negative (-) terminals.
Attempt Starting: Try starting the tractor.
Critical Warning: This method is exceptionally risky. Avoid unless you are an expert in tractor electrical systems and are certain of the procedure.
Comparing Jump-Starting Methods: Prioritize Safety
| Method | Safety Rating | Risk of Damage/Injury | Ease of Use | Reliability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Portable Jump Starter | High | Low | High | High | Medium |
| Jumper Cables | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium | Low |
| Screwdriver Bypass | Very Low | Very High | Low | Low | Very Low |
Preventative maintenance is the best approach. Regular care prevents breakdowns, saving time, money, and potential injury.
Preventative Maintenance: Avoiding Battery Failure
Key Takeaways:
- Regular cleaning of battery terminals prevents corrosion and extends battery life.
- Consistent voltage checks help monitor charge levels and prevent deep discharges.
- Visual inspections identify cracks, leaks, and other damage.
- A well-maintained battery significantly reduces the frequency of jump-starts.
- The right battery choice is crucial for longevity.
A dead battery leads to lost productivity and income. Regular maintenance is the key to preventing this.
Understanding Your Tractor Battery
Your tractor battery is crucial. Proper care extends its life (typically 3-5 years, but maintainable longer).
Cleaning and Voltage Monitoring
Regularly clean terminals (at least monthly) using a wire brush and baking soda solution to remove corrosion. Monitor voltage regularly using a multimeter; low voltage indicates a problem.
Visual Battery Inspections
Regularly inspect for cracks, bulges, leaks, or damage. Address any issues immediately.
Battery Selection
Invest in a quality battery. Consider cold cranking amps (CCA) and reserve capacity, especially for cold climates. AGM batteries often offer superior durability.
Charging Practices
Avoid overcharging using an automatic shutoff charger. Use the correct charger for your battery type. Overcharging can damage the battery.
By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the chances of a dead battery and keep your tractor running smoothly. Remember, even with preventative maintenance, knowing safe jump-starting procedures is essential for preparedness. When in doubt, consult a qualified mechanic.